LED light distribution refers to how light is spread from an LED fixture. This is a crucial factor in determining how well an area is illuminated. The fixture’s design, LED arrangement, and use of lenses or reflectors all play a role in shaping the distribution pattern. Choosing the right distribution ensures optimal visibility, efficiency, and aesthetics.
Table of Contents
Common LED Light Distribution Types
- Flood
Flood distribution spreads light over a wide area, making it perfect for large outdoor spaces like sports fields, parking lots, and building facades. These lights provide broad, even coverage, ensuring visibility and security. -
Spot
Spot distribution creates a narrow, intense beam, ideal for highlighting specific objects or areas. It’s commonly used in architectural lighting, stage lighting, and precision-focused illumination where targeted brightness is needed. -
Wall Wash
Wall wash distribution evenly lights vertical surfaces like walls or facades, making it perfect for decorative lighting. It enhances textures, architectural details, and visual appeal, commonly seen in museums, galleries, and commercial buildings. -
Linear
Linear distribution emits light in a straight line, designed for long, narrow spaces like hallways, pathways, and under-cabinet lighting. It provides consistent illumination along its length, improving visibility and aesthetics. -
Diffuse
Diffuse distribution spreads light evenly in all directions, creating soft, glare-free lighting. This type is best for ambient lighting in offices, retail spaces, and homes, ensuring a comfortable and well-lit environment. -
Area
Area distribution covers a broad, defined space, making it ideal for parks, parking lots, and open outdoor areas. This ensures uniform lighting coverage, improving safety and visibility in large environments.
Selecting the right light distribution is essential for achieving effective, efficient, and visually appealing lighting tailored to your specific needs.
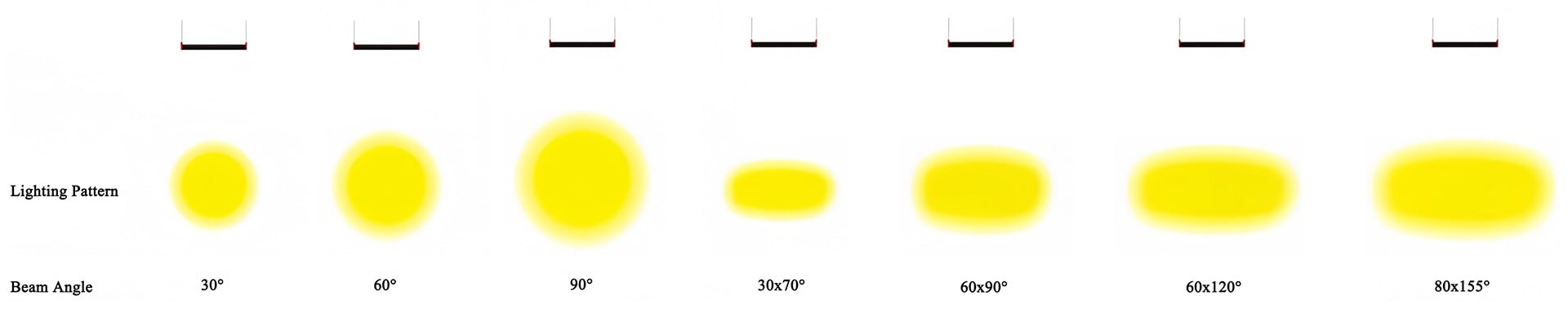
Factors to Consider When Choosing LED Light Distribution Types
Selecting the right LED light distribution is crucial for achieving optimal illumination, efficiency, and safety. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Area Size
- Larger Areas → Need wider light distributions to provide even coverage and eliminate dark spots. This is essential for parking lots, stadiums, and open outdoor spaces.
- Smaller Spaces → Benefit from focused, narrow beams to direct light where it’s needed most, preventing wasted illumination and improving energy efficiency.
2. Lighting Goals
- General Illumination → If the goal is to light up an entire space evenly, opt for wide-angle distributions such as flood or diffuse lighting.
- Task Lighting → For specific activities like reading, working, or highlighting objects, narrower beams (e.g., spot distribution) provide more concentrated and effective lighting.
3. Mounting Height
- High Mounting (e.g., streetlights, warehouse ceilings) → Requires wider beam angles to spread light efficiently over large areas.
- Low Mounting (e.g., under-cabinet lighting, indoor fixtures) → Works best with narrower beams to minimize glare and prevent light spillage.
4. Environmental Considerations
- Outdoor Lighting → Must account for weather conditions like rain, wind, and dust, which can impact performance. Higher IP-rated fixtures (e.g., IP65+) are better suited for harsh environments.
- Indoor Setups → Consider elements such as walls, furniture, or reflective surfaces that may block or redirect light, affecting the final illumination pattern.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure maximum efficiency, visibility, and lighting quality tailored to your specific application.
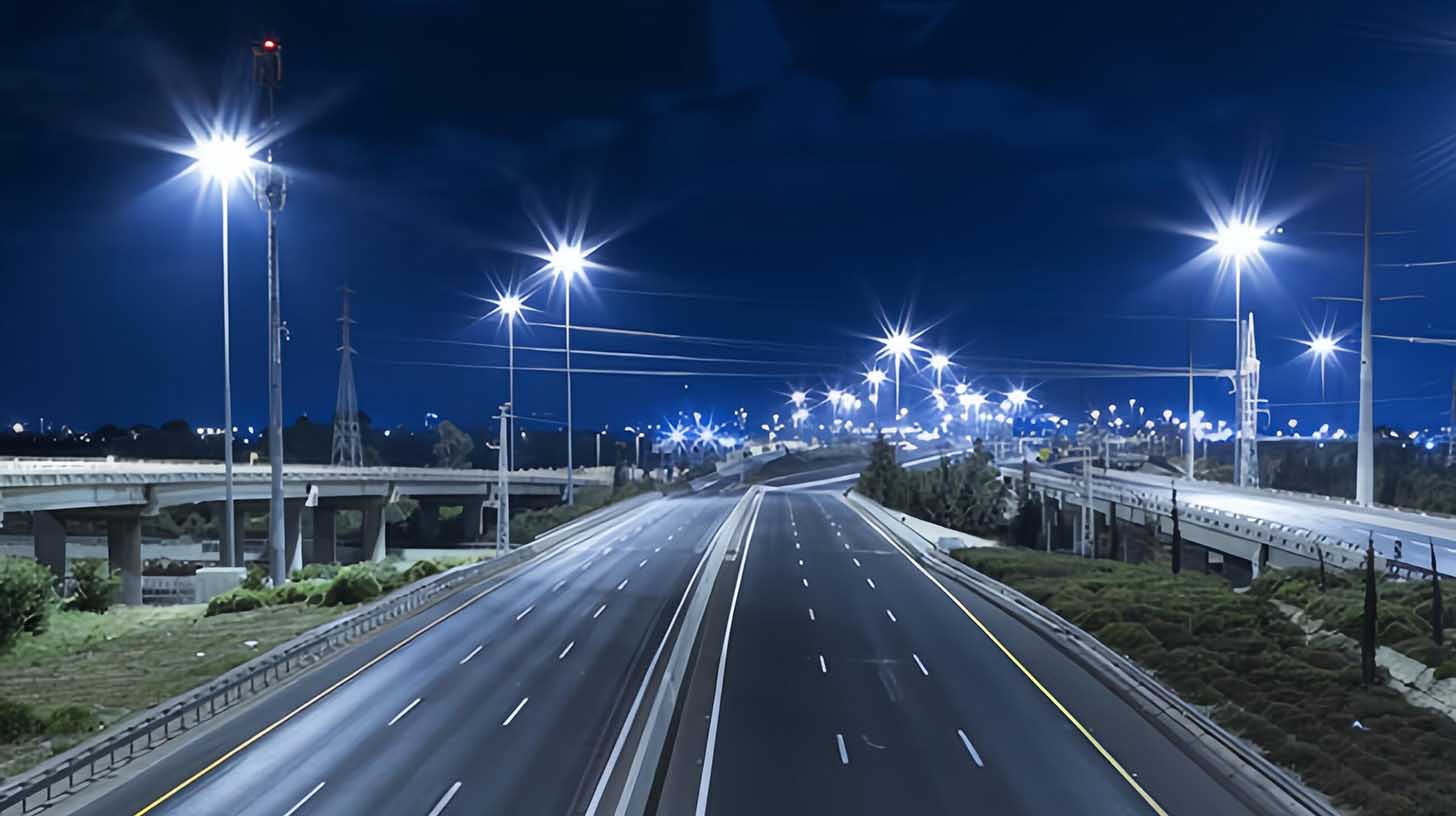

LED Light Distribution for Outdoor Area Lighting
The right LED light distribution is essential for outdoor area lighting, ensuring efficient illumination, energy savings, and reduced light pollution. Different distribution types cater to specific needs based on space size, shape, and purpose.
Common Outdoor Light Distribution Types
- Flood Distribution
- Ideal for wide-area illumination in sports fields, building facades, and construction sites.
- Provides powerful, broad coverage with adjustable angles to focus light where it’s needed.
-
Spot Distribution
- Best for highlighting monuments, architectural elements, or landscaping features.
-
Delivers a narrow, intense beam that enhances visibility and aesthetics with minimal spillover.
-
Type III Distribution
- Designed for parking lots, roadways, and large outdoor walkways.
-
Offers a forward and outward spread of light, covering large areas efficiently without excessive glare.
-
Type IV Distribution (Forward-Throw Lighting)
- Perfect for wall-mounted fixtures, building perimeters, and fence-line lighting.
-
Creates a semicircular light pattern, effectively illuminating open spaces near structures.
-
Type V Distribution
- Provides uniform, circular light distribution, ensuring consistent illumination in all directions.
- Ideal for parks, intersections, and large public spaces where even lighting is required.
By selecting the right light distribution pattern, you can achieve better visibility, improved safety, and optimal energy efficiency in outdoor environments.
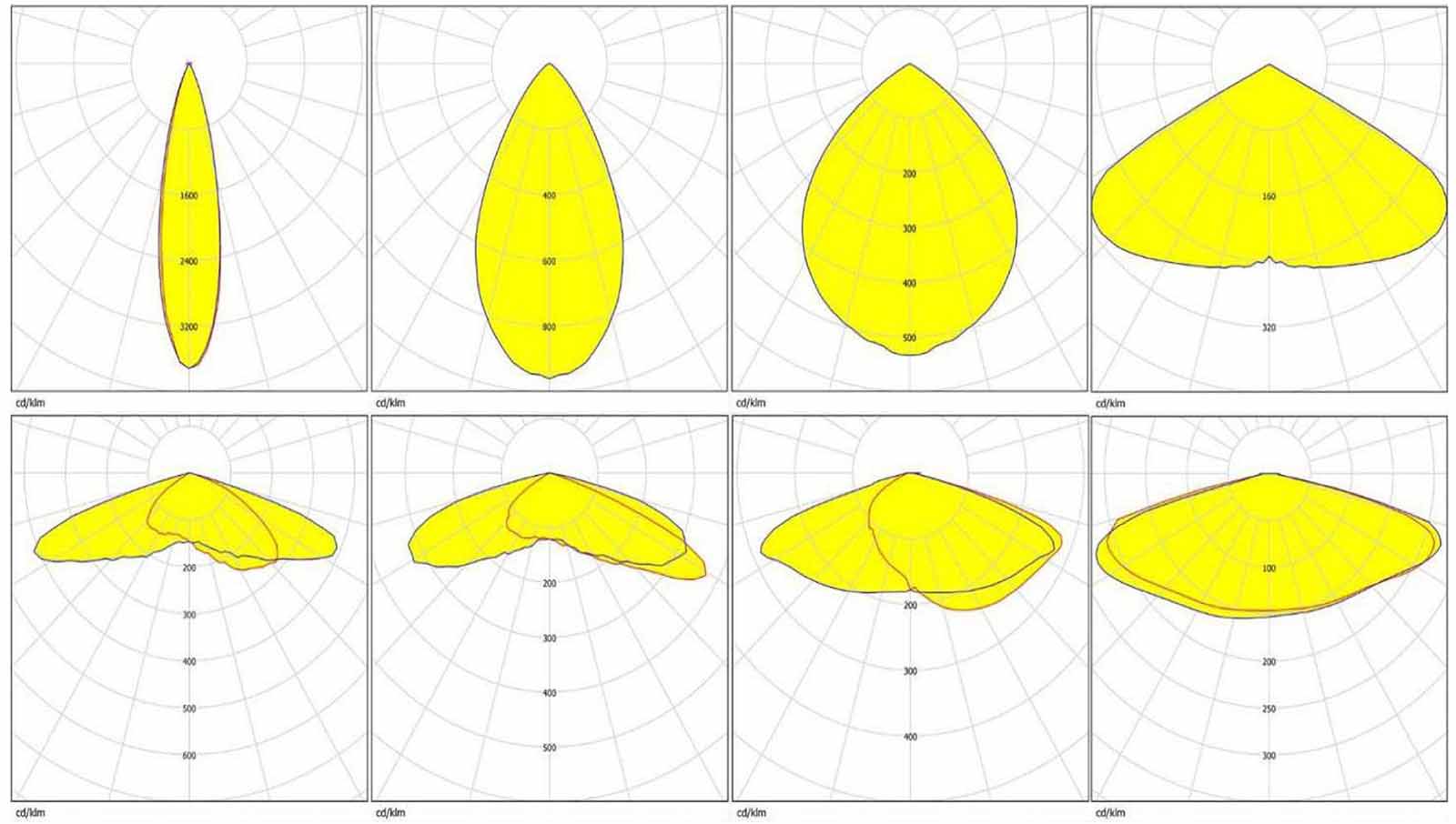
When choosing the right LED light distribution for outdoor areas, factors like fixture placement, mounting height, and application must be carefully considered. Proper distribution enhances safety, functionality, and aesthetics while minimizing glare and energy waste.
Learn more about What Are Light Distribution Types I, II, III, IV, V?.
How to Calculate the Number of LED Lights Needed
To determine how many LED lights are required for a space, consider the size, purpose, and lighting needs of the area. Follow these steps:
1. Measure the Area
- Calculate the total area in square meters (m²) or square feet (ft²).
- For rectangular spaces, use:
Area = Length × Width
2. Determine the Required Lumen Level
- Different spaces need different levels of brightness (lux = lumens per square meter). Examples:
- Residential Living Rooms → 200–300 lux
- Offices → 300–500 lux
- Warehouses → 150–250 lux
- Outdoor Sports Areas → 500–700 lux
- Multiply the area by the required lux level to calculate total lumens needed:
Total Lumens Needed = Area × Lux Level
3. Find the Lumen Output of Each Light
- Check the lumen output of the LED lights you plan to use (available in product specifications).
4. Calculate the Number of Lights
- Divide the total lumens needed by the lumen output of one light:
Number of Lights = Total Lumens Needed ÷ Lumen Output of One Light
5. Consider Spacing and Layout
- Ensure even light distribution by adjusting fixture placement:
- High ceilings → Require more powerful lights or closer spacing.
- Obstructions → May require additional fixtures for consistent coverage.
By following these steps, you can optimize illumination, improve efficiency, and avoid unnecessary energy use.
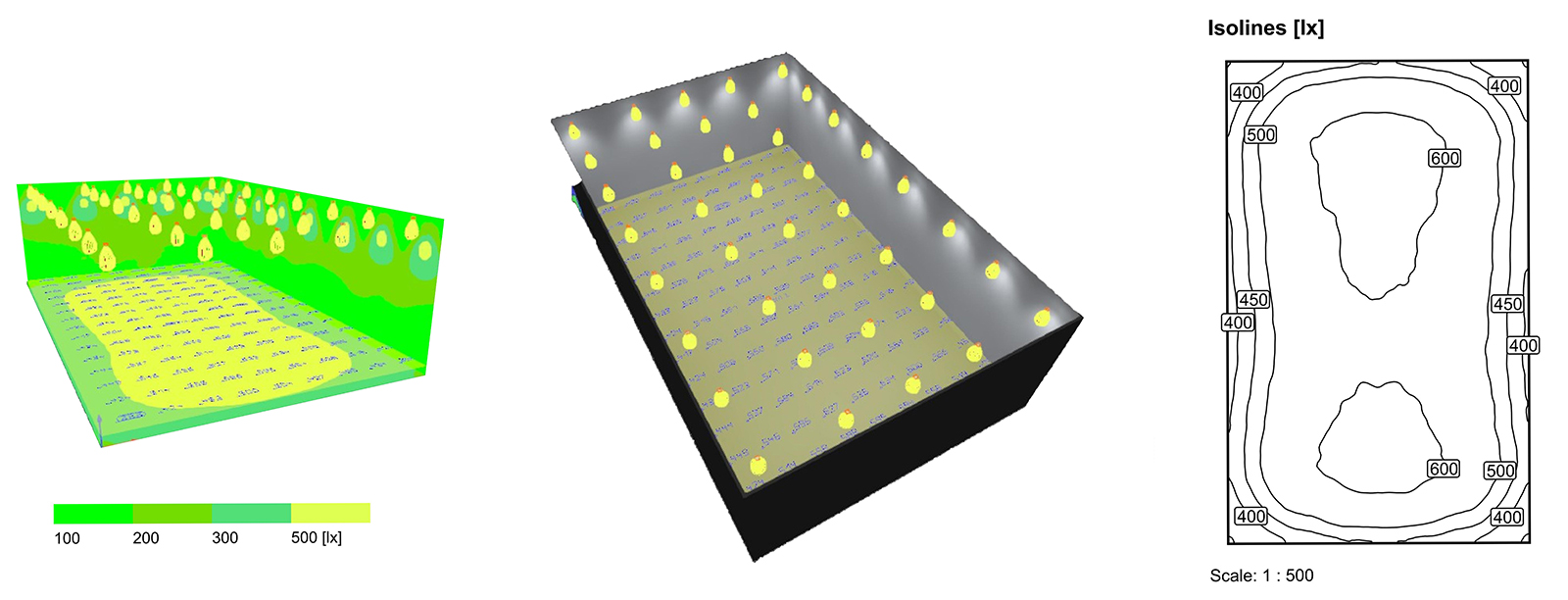
Example Calculation
- Scenario: A 50-square-meter office space requiring 400 lux. LED lights produce 1,600 lumens each.
- Area = 50 m²
- Required Lumens = 50 × 400 = 20,000 lumens
- Lumen Output per Light = 1,600 lumens
- Number of Lights = 20,000 ÷ 1,600 = 12.5 (~13 lights)
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the number of LED lights needed to achieve the desired brightness and functionality.
How to Choose the Right LED Light
Selecting the right LED light involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your specific needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Determine the Purpose
- Ambient Lighting: For general illumination in living rooms, offices, or hallways.
- Task Lighting: For focused lighting in work areas, such as reading lamps or under-cabinet lights.
- Accent Lighting: For decorative purposes, like highlighting art or architectural features.
2. Understand Brightness Needs
- LED brightness is measured in lumens—higher lumens mean brighter light.
- Example: 800 lumens is equivalent to a traditional 60W incandescent bulb.
- Match the lumen output to the room size and purpose:
- Bedrooms: 200–300 lux
- Kitchens or workspaces: 500–700 lux
3. Choose the Right Color Temperature
- Measured in Kelvins (K), color temperature affects how the light appears:
- Warm White (2,700K–3,000K) → Cozy, soft light for homes and restaurants.
- Cool White (4,000K–5,000K) → Bright and neutral for offices and task areas.
- Daylight (5,000K–6,500K) → Crisp, blue-tinted light for industrial areas or outdoor use.
Learn more about What’re Light Color Temperature – From Warm to Cool.
4. Consider Beam Angle
- Narrow angles (15°–30°) → Focused lighting, such as spotlights.
- Wide angles (60°–120°) → General lighting for larger areas.
5. Check the Fixture Compatibility
- Ensure the LED bulb or fixture is compatible with your existing fittings.
- For dimmable fixtures, choose a dimmable LED light.
6. Look for Energy Efficiency and Lifespan
- Check the wattage to ensure it’s energy-efficient while delivering adequate brightness.
- LEDs typically last 50,000 hours or more, reducing replacement costs.
7. Evaluate Quality and Certifications
- Choose LEDs with recognized certifications to ensure safety and reliability:
- CE (European safety standard)
- UL (North American safety standard)
- Energy Star (Efficiency and performance certification)
- Opt for LEDs with branded chips such as Lumileds and Osram.
- Use high-quality drivers like Meanwell for better stability and longevity.
8. Decide on Additional Features
- Smart Lighting: Control lights via apps or voice commands.
- Motion Sensors: Ideal for security and energy savings in outdoor or utility areas.
- Color-Changing Options: Great for decorative or mood lighting.
9. Test and Adjust
- Buy a sample before committing to a large purchase, especially for business or industrial applications.
- Test the light in its intended environment to ensure it meets your expectations.
By following these steps, you can choose an LED light that provides the best balance of brightness, efficiency, and longevity for your needs.

Conclusion
Choosing the right LED light distribution requires careful evaluation of your space’s size, lighting objectives, mounting height, and environmental conditions. Understanding different distribution types ensures your lighting is efficient, effective, and enhances safety and usability in any setting.
By considering these factors, you can create a well-optimized lighting system that minimizes glare, maximizes energy efficiency, and meets your specific needs.
If you need assistance with LED lighting solutions or have any questions, feel free to reach out to us. Our team of lighting experts is always ready to help.



