Uneven street lighting is a recipe for disaster. It creates dark spots, makes it harder to see, and increases the risk of accidents. Poorly distributed light turns roads into unpredictable hazards, leaving both drivers and pedestrians struggling to navigate safely. If street lighting isn’t uniform, it’s not doing its job. The key to safer roads is consistent, evenly spread illumination that eliminates harsh contrasts and provides clear visibility.
Street lighting uniformity is all about how evenly light is spread along a roadway, reducing the contrast between bright and dark areas. It’s measured using two key ratios: Overall Uniformity (U₀) and Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁). U₀ is the ratio of minimum to average illuminance, while U₁ is the ratio of minimum to maximum illuminance. Better uniformity means better road safety, compliance with lighting standards, and greater energy efficiency.
Keep reading to learn what uniformity means, how to calculate it, and what you can do to improve it for better street lighting design.
Table of Contents
What Does Uniformity Mean in Lighting?

Uneven lighting is more than just an eyesore—it causes visibility issues, eye strain, and unsafe conditions. Shadows and bright spots create an inconsistent lighting experience, reducing effectiveness and safety. The goal? Balanced, uniform illumination that enhances visibility and comfort.
Lighting uniformity is the even distribution of light across a surface, minimizing the contrast between bright and dark areas. It’s measured using uniformity ratios such as U₀ (minimum to average illuminance) and U₁ (minimum to maximum illuminance). Proper uniformity improves visibility, reduces glare, and enhances safety in roadways, parking lots, and public spaces.
Let’s break down exactly what light uniformity means and why it matters.
Light Uniformity Definition
Light uniformity is a measure of how evenly light is spread over an area. It plays a major role in road safety, workplace productivity, and visual comfort.
- High uniformity means consistent brightness with minimal variation.
- Low uniformity results in dark spots, glare, and poor visibility.
- Uniform lighting is crucial for street lighting, parking lots, warehouses, and sports facilities.
When lighting is well-distributed, it eliminates harsh contrasts, reduces glare, and ensures better visibility and safety.
Light Uniformity Factor
Uniformity isn’t just a guessing game—it’s measured using specific ratios that define how evenly light is spread across a given area. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Overall Uniformity (U₀)
- Measures how consistent the lighting is across the entire area.
- Formula:
U₀ = E_min / E_avg - E_min = Minimum illuminance
- E_avg = Average illuminance
- A higher U₀ value means better uniformity.
2. Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁)
- Evaluates brightness variations along the road’s length.
- Formula:
U₁ = E_min / E_max - E_min = Minimum illuminance
- E_max = Maximum illuminance
- Used primarily for roadway lighting to ensure smooth brightness transitions and avoid sudden shifts in visibility.
3. Target Uniformity (U_t)
- Measures how well specific areas receive the required illumination.
- Ensures that critical zones (like pedestrian crossings or intersections) get enough light.
Good uniformity prevents glare, improves visibility, and enhances energy efficiency—all while making roads and public spaces safer.
Lighting that’s evenly distributed makes a huge difference. Next, we’ll dive into how to calculate lighting uniformity and the best ways to improve it.
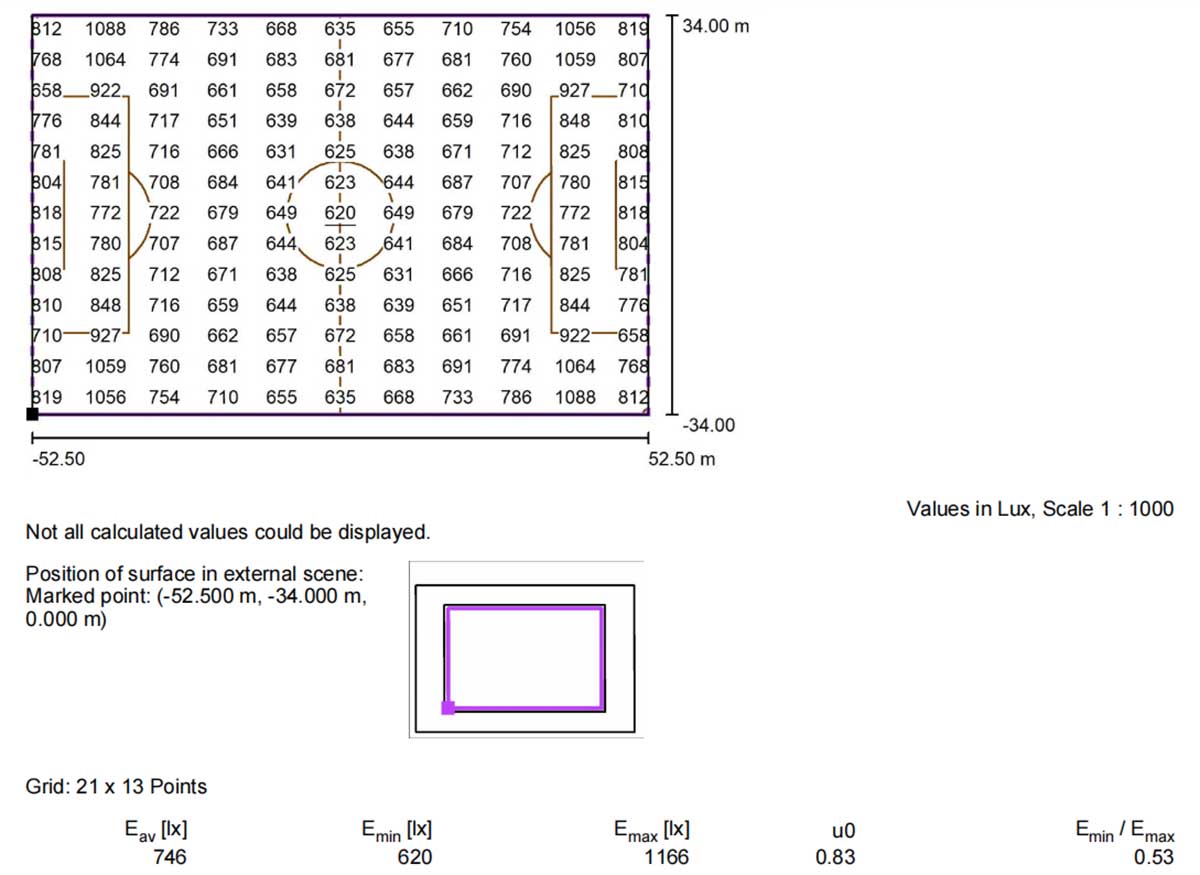
Lighting Uniformity Measurement
How to Calculate Light Uniformity?
Light Uniformity Measurement
Measuring light uniformity is all about checking how evenly light spreads across a surface. If some areas are too bright while others are too dim, visibility suffers. That’s why proper measurement is key—it ensures lighting is effective, safe, and meets required standards.
1. Tools for Measuring Light Uniformity
- Lux Meter – Measures illuminance at different points across the surface.
- Lighting Simulation Software – Creates detailed uniformity calculations before installation.
- Lighting Uniformity Calculator – Online tools that estimate uniformity based on input data.
2. Steps for Measuring Uniformity
a. Select Measurement Points
- Divide the area into a grid pattern for accurate readings.
- Ensure equal spacing between measurement points for consistency.
b. Record Illuminance Values
- Use a lux meter to measure brightness levels at each grid point.
- Make sure readings are taken at the same height and angle for accurate results.
c. Identify Minimum, Maximum, and Average Illuminance
- E_min: The lowest recorded brightness level.
- E_max: The highest recorded brightness level.
- E_avg: The average brightness across all measurement points.
d. Apply Uniformity Formulas
- Use the U₀ and U₁ formulas to calculate how evenly light is distributed.
Accurate measurement ensures that lighting installations meet industry standards for safety, efficiency, and performance.

Light Uniformity Formula
Light uniformity isn’t something you eyeball—it’s calculated using two key formulas: Overall Uniformity (U₀) and Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁).
1. Overall Uniformity (U₀)
- Formula:
U₀ = E_min / E_avg - Definition: Measures how well the minimum brightness compares to the average brightness across the area.
- Ideal Values:
- Highways: U₀ ≥ 0.4
- Major Roads: U₀ ≥ 0.35
- Residential Streets: U₀ ≥ 0.3
A higher U₀ means more even lighting and fewer dark spots.
2. Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁)
- Formula:
U₁ = E_min / E_max - Definition: Measures how smoothly brightness is distributed along a road’s length.
- Ideal Values:
- High-Speed Roads: U₁ ≥ 0.6
- Pedestrian Walkways: U₁ ≥ 0.4
A higher U₁ means fewer drastic brightness changes, making roads safer.
3. Example Calculation
Let’s say we have a roadway with the following readings:
- E_min = 12 lux
- E_avg = 40 lux
- E_max = 80 lux
Applying the formulas:
- U₀ = 12 / 40 = 0.3
- U₁ = 12 / 80 = 0.15
These values indicate that the lighting uniformity needs improvement to meet roadway safety standards.
4. Factors Affecting Uniformity
- Pole Spacing: Closer poles help maintain even lighting.
- Mounting Height: Higher fixtures spread light better but may reduce intensity.
- Beam Angle Selection: Wider beam angles improve uniformity but may require adjustments.
By following these calculations and best practices, lighting engineers can optimize uniformity for safer roads, better visibility, and greater energy efficiency.

What Is the Uniformity of Road Lighting?
Bad road lighting isn’t just inconvenient—it’s dangerous. It creates dark spots, glare, and visibility problems that increase the chances of accidents. If uniformity is off, roads become unpredictable, making it harder for drivers and pedestrians to stay safe. Proper lighting uniformity eliminates these risks, ensuring smooth, consistent illumination across the roadway.
Importance of Road Lighting Uniformity
Even lighting is crucial for:
- Driver Safety – Prevents sudden brightness changes that can cause visual discomfort.
- Pedestrian Protection – Ensures crosswalks and sidewalks remain well-lit.
- Accident Prevention – Eliminates dark zones where hazards might go unnoticed.
- Energy Efficiency – Reduces the number of fixtures needed while maintaining visibility.
Road lighting should always be designed for consistent brightness, avoiding glaring hot spots or dangerously dark areas.
Key Road Lighting Uniformity Measurements
Roadway uniformity is measured using specific ratios that determine how well light is distributed.
1. Overall Uniformity (U₀)
- Formula:
U₀ = E_min / E_avg - Definition: Measures how evenly light is spread across the road.
- Recommended Values:
- Highways: U₀ ≥ 0.4
- Major Roads: U₀ ≥ 0.35
- Residential Streets: U₀ ≥ 0.3
A higher U₀ value means better uniformity and fewer visual distractions for drivers.
2. Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁)
- Formula:
U₁ = E_min / E_max - Definition: Measures how well light is distributed along the road’s length, preventing drastic brightness variations.
- Recommended Values:
- High-Speed Roads: U₁ ≥ 0.6
- Urban Roads: U₁ ≥ 0.5
A higher U₁ keeps brightness transitions smooth, reducing eye strain for drivers.
Recommended Uniformity Standards for Road Lighting
Uniformity needs to be adjusted depending on road type and traffic volume. Here are the standard values:
| Road Type | Overall Uniformity (U₀) | Longitudinal Uniformity (U₁) | Average Lux (E_avg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Highways | ≥ 0.4 | ≥ 0.6 | 20 – 30 lux |
| Major Roads | ≥ 0.35 | ≥ 0.5 | 15 – 25 lux |
| Residential Streets | ≥ 0.3 | ≥ 0.4 | 5 – 15 lux |
| Pedestrian Walkways | ≥ 0.25 | ≥ 0.4 | 5 – 10 lux |
Meeting these uniformity standards ensures that roadways are well-lit, reducing accident risks and improving visibility for all road users.

How to Improve Road Lighting Uniformity?
If you want to fix uneven road lighting, you need the right approach. Here’s how to make sure streetlights provide consistent, balanced illumination without dark spots or glaring hotspots.
1. Optimize Pole Placement and Spacing
- Evenly spaced poles ensure uniform coverage and prevent dark patches.
- Adjust pole height based on the width of the road and required brightness levels.
2. Use Asymmetric Optics for Even Light Distribution
- Asymmetrical beam angles help spread light evenly across the roadway.
- Avoid excessive overlap—too much light in one area creates unnecessary glare.
3. Select the Right LED Street Light Fixtures
- Choose LEDs with high efficiency (≥ 130lm/W) to improve coverage without wasting energy.
- Adjust color temperature (4000K – 5000K) to enhance road visibility and driver comfort.
4. Incorporate Smart Lighting Controls
- Adaptive dimming automatically adjusts brightness based on traffic conditions.
- Motion sensors enhance safety in pedestrian zones and crosswalks.
Using these strategies, you’ll get better uniformity, lower energy costs, and safer roads.
What Is the Uniformity of Parking Lot Lighting?
Parking lots need a higher level of uniformity to keep pedestrians and drivers safe. Poor lighting creates shadows and blind spots—major safety risks in busy parking areas. Here’s what’s recommended:
| Parking Lot Type | Uniformity Requirement (U₀) |
|---|---|
| High-Security Areas | ≥ 0.5 |
| General Parking | ≥ 0.3 |
| Low-Traffic Areas | ≥ 0.25 |
Better uniformity means fewer shadows, less glare, and improved overall visibility.
What Is the Standard Lux for Street Lighting?
Different roads need different brightness levels. Here are the standard lux recommendations to ensure proper illumination:
| Road Type | Recommended Lux Levels |
|---|---|
| Highways | 15 – 30 lux |
| Major Roads | 20 – 40 lux |
| Residential Streets | 5 – 20 lux |
| Parking Lots | 10 – 50 lux |
These numbers ensure that roads are bright enough for safety while keeping energy use efficient.
What Are the Requirements of Good Street Lighting?
A well-designed street lighting system needs to meet certain safety, efficiency, and performance standards:
- High Uniformity (U₀ ≥ 0.4 for highways, ≥ 0.3 for residential streets).
- Adequate Lux Levels (Matched to road type and application).
- Minimal Glare (Use proper optics and shielding to reduce eye strain).
- Directional Lighting (Prevents wasted light and reduces light pollution).
- Energy Efficiency (LED street lights with smart controls cut down on power consumption).
Following best practices in street lighting design ensures safer roads and lower operational costs.

Conclusion
Uniform street lighting isn’t just about brightness—it’s about safety, efficiency, and visibility. Poorly distributed lighting leads to accidents and wasted energy, while well-planned lighting improves road safety and reduces costs.
By getting the right spacing, beam control, and smart technology, cities can achieve top-tier lighting uniformity.
If you’re looking for high-quality LED street lights that meet the highest standards in uniformity and efficiency, contact us today! Let’s build safer, brighter streets together.




