If you’ve ever had lights that flicker or don’t dim consistently, you’re not alone. Poor dimming control can cause a lot of problems. It can make your people unproductive. It can make it so your lights don’t save you energy. It can make your customers unhappy. But, if you understand 0-10V dimming, you can have better control of your lights. That’s what we’re going to talk about today.
0-10V dimming is a way to adjust the light output of a light-emitting diode (LED) light. It is done by changing the DC voltage on the control wires of the LED. This guide covers what you need to know about 0-10V dimming, how to wire a 0-10V dimmer switch, and troubleshooting tips.
Stay tuned to learn about the technicalities and practical tips for using 0-10V dimming in your LED lighting projects.
Table of Contents
What is 0-10V Dimming?
0-10V dimming is a way to control the brightness of LED lights and other types of lights. It’s done using a simple control signal that goes from 0 to 10 volts. When it’s at 0 volts, the lights are completely off. As you turn the voltage up, the lights get brighter and brighter until they’re at full power at 10 volts.
You’ll often see this type of dimming used in commercial and industrial applications where they need to have adjustable lighting. It allows them to change the brightness of the lights without them flickering, which saves energy and makes people happy. You can use a dimmer switch or a lighting control system to control the lights. It’s easy to use, and it works great.
Key points of 0-10V Dimming
Turns lights on and off by varying voltage from 0V (all the way off) to 10V (full on)
Dimming technology using low voltage DC signals
Works with lots of LED drivers and fixtures
How 0-10V Dimming Works
0-10V dimming is a simple and effective way to control the brightness of LED lights. It’s done through a low-voltage control signal that goes from 0 to 10 volts. When it’s at 0 volts, the lights are off. When it’s at 10 volts, the lights are as bright as they can be.
Here’s how it works. You send a signal from a dimmer switch to a driver that’s inside the LED fixture. The driver adjusts the amount of power that goes to the LEDs based on the signal it gets from the dimmer switch. Because it’s an analog system, it allows you to dim the lights without them flickering. This technology is used in commercial applications where they need to have adjustable lighting. Think of an office or a retail store. It gives you flexibility and allows you to save money on electricity.
Wiring and Installation
To wire up and install a 0-10V dimming system, you need to do a simple 4-wire setup. You have two wires for your AC power, and you have two low-voltage wires that go to your dimming signal. Those wires are usually purple and gray.
To install it, you connect your dimmer to your AC power supply. Then you connect your LED driver to both your dimmer and your LED fixture. The driver reads the signal from the dimmer and adjusts the power going to the LEDs accordingly. This setup allows you to control the brightness of the lights and have them dim smoothly without flickering. It gives you a great lighting experience while saving energy. It’s important to install the system correctly so that it works right and keeps working.
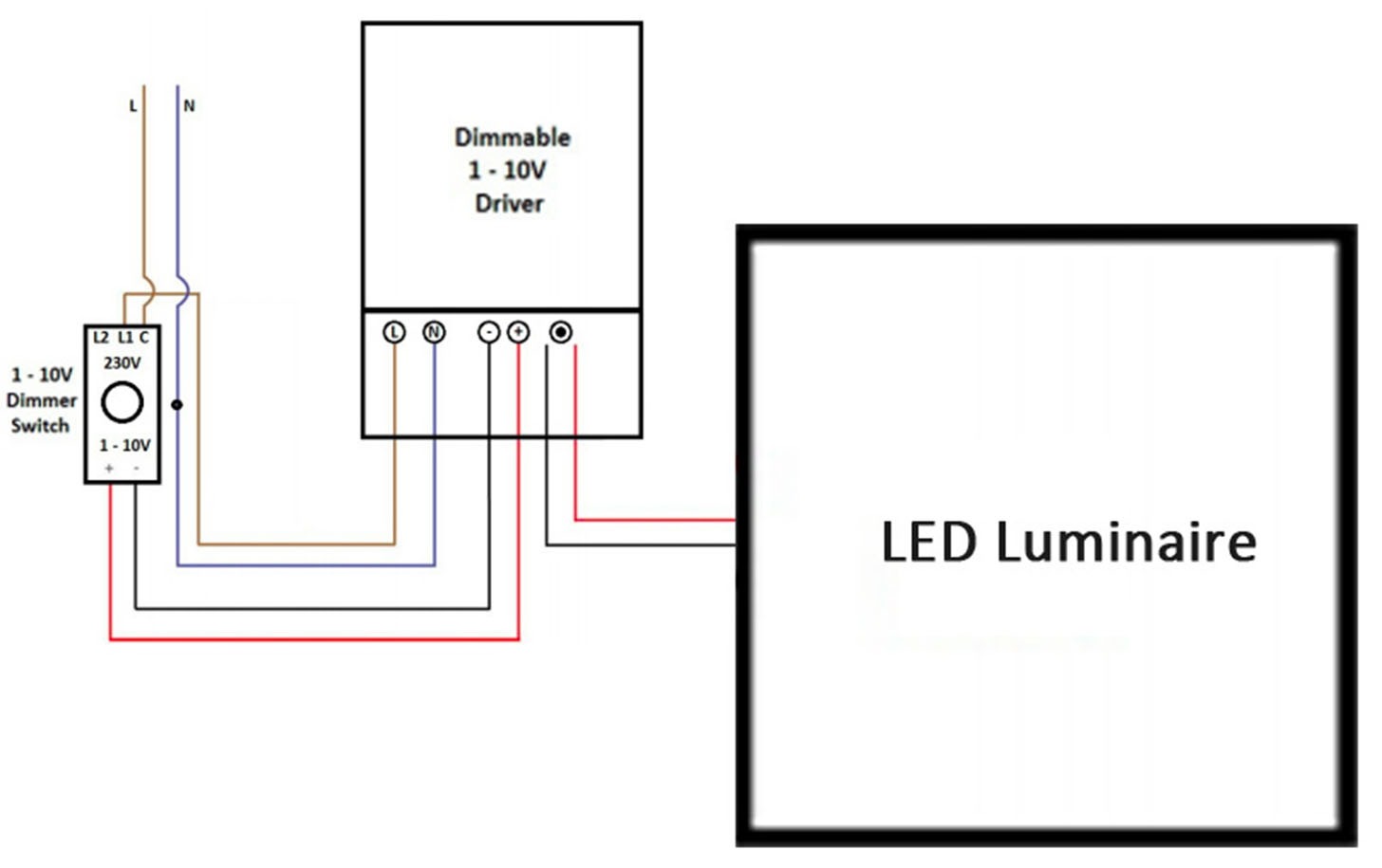
0-10V Dimming Wiring Dragram
Advantages of 0-10V Dimming
Here are several reasons why 0-10V dimming is a popular way to control LED lights:
Simple and Reliable Technology: Because it’s an analog technology, 0-10V dimming is simple and reliable. There’s not much to it, so you don’t have much that can go wrong with it.
Wide Compatibility: It’s compatible with most LED products, so it’s a great technology to choose for your commercial and industrial lighting needs. It works with all kinds of LED drivers and dimmers, so you can install it in new stuff or retrofit it into your existing stuff.
Ease of Installation and Use: The wiring is easy. It’s just a 4-wire setup. You have two wires for power, and you have two low-voltage signal wires. The wiring is usually pretty straightforward, so it’s easy to install.
Precise Brightness Control: You can control the brightness of the lights from full blast to almost nothing. That means you can create the perfect mood or get the lighting just right for what you’re doing.
Energy Efficiency: When you turn down the lights, you save energy. This can save you a ton of money, especially if you have a lot of lights or you dim them a lot.
Cost-Effective Solution: Because it’s a common and standard technology, 0-10V dimming is usually cheaper than other fancy dimming technologies. It doesn’t cost much to put in, and it doesn’t cost much to maintain.
No Limit on Load Size: There’s no limit to the size of the load you can control with 0-10V dimming. You can control as many fixtures as you want. This is awesome for large spaces like warehouses or big commercial buildings.
These things make 0-10V dimming a great choice for a lighting system where you need to have dependable, energy-efficient, and user-friendly dimming control.
Applications of 0-10V dimming
Commercial and Industrial Lighting: In warehouses, factories, and big places, 0-10V dimming is a great way to control the lights. You can make the lights brighter or dimmer based on the time of day, if there are people there, or what they’re doing. It saves energy and helps keep people safe.
Office Spaces: Offices are a great place for 0-10V dimming because you can set the lights to be comfy all day long. You can also save people’s eyeballs by turning the lights down. This can help people focus, be more productive, and be more comfortable. This is especially true if you have windows in your office or if you have areas in your office that need both task and ambient lighting.
Retail Environments: In retail, lighting is critical to set the mood and show off your stuff. 0-10V dimming allows you to make the lights brighter or dimmer based on the time of day, what you’re promoting, or what part of your store you want to highlight. You can save energy and make your customers happy at the same time.
Outdoor Lighting: 0-10V dimming is perfect for outdoor applications like parking lots, the outside of your building, and landscape lighting. You can set the lights to be brighter when people are around and turn them down when nobody’s there. That way, your parking lot stays lit up for safety, but you’re not wasting a ton of energy.
Multi-Purpose Spaces: In conference rooms, auditoriums, and places where you have events, 0-10V dimming is awesome. You can make the lights do what you want for your presentations, performances, or parties.
In each of these places, 0-10V dimming helps you save money on your electric bill and lets you make your lights do what you want them to do. That’s why 0-10V dimming is a great choice for so many different places.

Standards and Types of 0-10V dimming
There are two main standards for 0-10V dimming. They are IEC 60929 Annex E and ESTA E1.3. The two standards use different ways to send the control signal, so they don’t work with each other. You need to make sure all the stuff you get is the same kind.
IEC 60929 Annex E (Current Sink Method): This is the most common standard used by commercial fluorescent and LED lighting. It works on the “current sink” principle. The dimmer sucks up a little bit of current that the driver or ballast sends out. The amount of current the dimmer sucks up changes as the voltage going to the dimmer changes between 0 and 10 volts. Most of the 0-10V LED drivers out there use this current sink method.
ESTA E1.3 (Current Source Method): This is the standard developed by the Entertainment Services and Technology Association. It works on the “current source” principle. The dimmer sends out a little bit of current to the driver instead of sucking it up. This standard is more common in theatrical and stage lighting. This standard is more specific to theatrical and stage lighting where you need more precise control and want it to work with as much stage lighting equipment as possible.
Because the two standards are not compatible with each other, you can’t mix and match the different components. If you do, bad things will happen. That’s why it’s important to make sure that all of your dimmer switches, drivers, and everything else are the same standard.

0-10V dimming vs other dimming technologies like DALI or DMX
0-10V dimming is easy and it works. It is not like the more advanced digital dimming technologies like DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) or DMX (Digital Multiplex). Each one of these has its own strengths and the applications where it works best.
Control Precision and Flexibility:
0-10V is an analog system. It’s a nice, smooth way to make the lights brighter and dimmer. However, with 0-10V, all of the lights go up and down together. You can’t program each light to do its own thing. That’s great if you want all the lights to do the same thing like in an office or a warehouse.
DALI is a digital protocol that lets you do all of this cool stuff. You can make each light brighter or dimmer, turn it on or off, or set it to a specific scene. This is great for places like an office, a hospital, or a hotel where you want to have different scenes and different zones of lighting. Learn more about How Does DALI Lighting Work? – A Comprehensive Guide
DMX is even more granular than DALI. It is used in theatrical, entertainment, and architectural lighting. It can control hundreds of channels at the same time in real time. DMX is designed for things like color changes and scene changes. That makes it perfect for stages and events. Here is more about What’s DMX? – A Brief Introduction of DMX512 Digital Lighting Control System
Communication and Feedback:
0-10V is a one-way communication system. The dimmer sends a signal to the driver, but the driver doesn’t send any signal back to the dimmer. This makes it hard to troubleshoot or monitor your lights because you can’t tell if they’re on or off or anything else about them.
With DALI, you get two-way communication. The driver can tell you what’s going on with the light. This makes it easy to see if the power is on or off, if there’s an error, or if the dimming level is where you want it. If you have a big lighting system, this is a great way to keep track of everything.
DMX is another one-way protocol. It is used for precise, high-speed control. There is not any built-in two-way communication with DMX. Some external systems can monitor DMX, but it’s not built into the system like it is with DALI.
System Complexity and Installation:
0-10V is easy and inexpensive. You just need to run the wires for power and for the dimming signal. It’s easy to install and is great for applications where you don’t need a lot of fancy features.
DALI is more complicated. You have to install special controllers and each driver has to have an address. It’s more expensive to install, but it’s worth it if you need a lot of customization and flexibility.
DMX is complicated. You have a ton of channels and a ton of control options. You need special controllers for DMX. However, if you need to be creative with your lights, the complexity is worth it.
Here’s the bottom line:
0-10V dimming is simple and cheap. Use it if you need basic dimming.
DALI is for commercial stuff where you need to control each light, see if it’s on, and set up detailed scenes.
DMX is for fast, real-time control of a bunch of different lights.
Here’s a table comparing 0-10V, DALI, and DMX:
| Feature | 0-10V Dimming | DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) | DMX (Digital Multiplex) |
| Type of Control | Analog | Digital | Digital |
| Control Precision | Group-level dimming (all fixtures together) | Individual fixture control with addressable fixtures | High-precision, multi-channel control |
| Communication | One-way (no feedback) | Two-way (supports fixture status feedback) | One-way, but external feedback systems can be added |
| Minimum Dimming Level | Varies by product (e.g., 10%, 1%, or 0.1%) | Precise, down to very low levels | Can dim to zero or minimum, depends on fixture |
| Setup Complexity | Simple (4-wire system) | Moderate to high complexity, requires controllers and addressing | High complexity, requires channel mapping and controllers |
| Scene and Zone Control | Limited (no scenes or zones) | Advanced scene and zone control possible | Advanced scenes and live transitions |
| Ideal Applications | Basic commercial and industrial spaces, offices, warehouses | Complex lighting setups in offices, hospitals, hotels | Theaters, stages, architectural lighting, entertainment |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate (no automated scheduling) | High (supports automated schedules and monitoring) | Moderate to high (suitable for creative control) |
| Installation Cost | Low | Moderate to high | High |
| Maintenance and Monitoring | Basic (manual monitoring) | Advanced (remote monitoring and diagnostics) | Basic, though feedback systems can be integrated |
| Best for Dynamic Effects | No | No | Yes (ideal for dynamic scenes and color changes) |
| Examples of Control Levels | 0V = off, 10V = full brightness | Percentage-based control, programmable | 0-255 channel values, allowing granular brightness |
More Considerations of 0-10V dimming
If you’re using 0-10V dimming, here are a few more things to think about:
Minimum Dimming Levels: Different 0-10V dimming products can dim to different minimum levels. Some can only dim down to 10% of full brightness. Others can dim down to 1% or even 0.1%. Make sure you get products that will dim as low as you need them to go. For example, if you’re doing a theater or a presentation room where you need it to be really dark, you might want to have lights that can dim to 1% or even lower.
Separate Switch for On/Off: In a lot of 0-10V systems, when you turn the lights all the way down to 0V, they don’t turn off. They go as low as they can go, but they don’t turn off. If you need the lights to be all the way off, you’ll need to have a separate on/off switch. This is important if you want to save energy or need total darkness at times.
Limited Features Compared to Digital Protocols: Unlike DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) or DMX (Digital Multiplex), which allow you to do all kinds of cool stuff—like set up scenes, address each light, and have two-way communication—0-10V dimming is more basic. It’s a super reliable way to dim your lights. If you need to do a lot of fancy stuff with your lights, you might want to use a digital protocol instead.
These are important things to know about 0-10V dimming.
FAQs about 0-10V Dimming
What are the requirements for 0-10V dimming?
To use a 0-10V dimming system, you need to have LED fixtures that are compatible with 0-10V dimming. You need a 0-10V dimmer switch. You need to wire everything correctly. You have two control wires that go between the dimmer and the driver. You need to make sure your LED fixtures have a 0-10V driver that works with this system.
How many fixtures can be on a 0-10V dimmer?
It depends on the current output capacity of the dimmer and the control circuit requirements of your fixtures. Most dimmers can handle several fixtures, but you can’t go crazy. If you have too many fixtures on a dimmer, they may flicker or not dim correctly. Look at the specifications for your dimmer and add up the total load of all the fixtures you have connected to it.
What is the major disadvantage of controlling different groups of luminaires using a 0-10V dimming system?
One drawback to using 0-10V dimming to control multiple groups of fixtures is that you don’t have zone control. Since all the fixtures on the 0-10V circuit dim at the same time, you can’t have different dimming levels in different areas unless you run separate 0-10V circuits to different areas. This lack of zone control can be a big deal if you need to have fine control over the lighting in different areas.
How far can you run a 0-10V dimming cable?
The maximum distance for 0-10V dimming cables is usually 300 feet. If you run cables longer than this, you may get voltage drop, which will screw up your dimming and make your lights not look the same. If you need to run longer distances, use a higher gauge wire to reduce voltage drop or use a control relay to boost the signal.
What cable do I need for 0-10V dimming?
0-10V dimming typically needs a two-wire control cable. Each wire in the cable needs to be rated to handle the low-voltage DC signal. Most people use standard 18 AWG stranded or solid copper wire, but check the dimmer manufacturer’s specifications to be sure. Using shielded cables can help reduce the amount of interference you might get, especially if you are in an environment with a lot of electrical noise.
How to troubleshoot 0-10V dimming?
If you’re having 0-10V dimming issues, check your wiring connections for loose or incorrect connections. Make sure your dimmer switch is compatible with your LED fixtures. Measure the control voltage across the dimming wires to make sure it matches what it should be. If you have flickering, check to see if your load is within the maximum capacity of your dimmer.
What color code is 0-10V dimming?
For most 0-10V dimming systems, the standard color code is purple for the positive dimming control wire (+) and gray for the negative dimming control wire (-). However, make sure you check your fixture and dimmer documentation to see what colors they use.
How many watts can a 0-10V dimmer handle?
The wattage capacity of a 0-10V dimmer depends on the model, but many of them can handle up to 800 watts or more. You need to check the specifications of your dimmer switch and add up the total wattage of all the fixtures you have connected to it to make sure you don’t overload it. If you overload your dimmer, it may overheat, flicker, or stop working.
Does 0-10V dimming wire need to be shielded?
While 0-10V dimming wire doesn’t always need to be shielded, it is a good idea to use shielded cable in environments with a lot of electrical noise. Shielded cable helps prevent signal degradation, which can cause flickering or inconsistent dimming. If your installation is near large motors or high-voltage power lines, use shielded cable.
Can I use a regular dimmer on 0-10V?
No, you cannot use a regular dimmer switch designed for line-voltage AC systems on a 0-10V system. 0-10V dimming uses a low-voltage DC signal, which is incompatible with standard AC dimmers. If you use the wrong dimmer switch, you can damage your fixtures and possibly create a safety hazard.
Does 0-10V dimming flicker?
Yes, 0-10V dimming is normally smooth and flicker-free if you install everything right and don’t overload the system. If you run long cable runs, you can get flickering from a voltage drop. You can also get flickering from interference with other devices. Finally, you can get flickering if you have too many fixtures on your dimmer switch. Use good-quality stuff and wire everything up right, and you’ll have no problems.
Is 0-10V dimming AC or DC?
0-10V dimming is a DC (direct current) control method. The control wires carry a low-voltage DC signal that varies from 0V to 10V. This signal tells the fixture how much light to put out. This method gives you fine control over your light levels without all the crap that comes with AC dimming.
What are the advantages of 0-10V dimming?
The benefits of 0-10V dimming include precise control over your light levels, compatibility with a wide range of LED fixtures, and smooth, flicker-free dimming. It’s also easy to install and use, which makes it great for commercial and industrial applications where you want to save energy and have good control over your lights.
How to test a 0-10V signal?
To test a 0-10V signal, use a multimeter and measure the voltage between the two dimming control wires (usually purple and gray). A voltage of 10 volts means the lights are at full brightness, and 0 volts means the lights are at their minimum brightness level. This test will tell you if your dimmer switch and your wiring are working correctly.
Is 0-10V analog or digital?
0-10V dimming is an analog control system. The voltage on the control line represents a wide range of dimming levels. This is different than a digital system, which uses binary signals. With 0-10V dimming, you get smooth, linear dimming. This type of dimming is great for applications where you want to make precise, gradual changes to your light levels.
What is the maximum distance for 0-10V dimming?
The maximum distance for 0-10V dimming cables is around 300 feet. If you go beyond this distance, you may get voltage drop and your lights may not dim consistently. If you have to go longer distances, use a thicker gauge wire or consider adding signal boosters to keep your dimming performance where you want it.
How is 0-10V dimming wired?
In a typical 0-10V dimming setup, you’ll have two low-voltage control wires (purple for positive, gray for negative) that go from your dimmer switch to your LED driver. These are the wires that control the light output based on the voltage level. Then you’ll have your main power wires that supply AC to your fixture. Remember to always follow the wiring diagram that comes with your fixtures to make sure you wire everything up correctly.
Why do we use 0-10V?
The reasons 0-10V dimming is so popular are because it’s simple, reliable, and compatible with many different LED lighting systems. It provides smooth, flicker-free dimming and gives you precise control over your lights. For these reasons, it’s perfect for commercial and industrial applications where you want to save energy and have good-quality lighting.
Conclusion
Understanding 0-10V dimming is critical for anyone working with LED lighting. From knowing how to wire everything up and how to troubleshoot problems to the benefits of smooth, flicker-free control, 0-10V dimming is the bomb. Whether you’re a lighting contractor, an engineer, or a facility manager, knowing how to set up and maintain 0-10V dimming will help you get great lighting results on all your projects.
Dimmable LED Lights – A Guide To Different Dimming Systems
What are the Different Types of Lighting Control?
DALI and 0-10V Dimmable LED Panel Lights
DALI Dimming: 7 Frequently Asked Questions for Smart Lighting
How Does DALI Lighting Work? – A Comprehensive Guide
Request A Free Quote Now!
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!