Are you having problems with electrical safety and efficiency? Poor lighting choices can create significant safety issues and operational inefficiencies. Do you know the differences between Class I, II, and III luminaires?
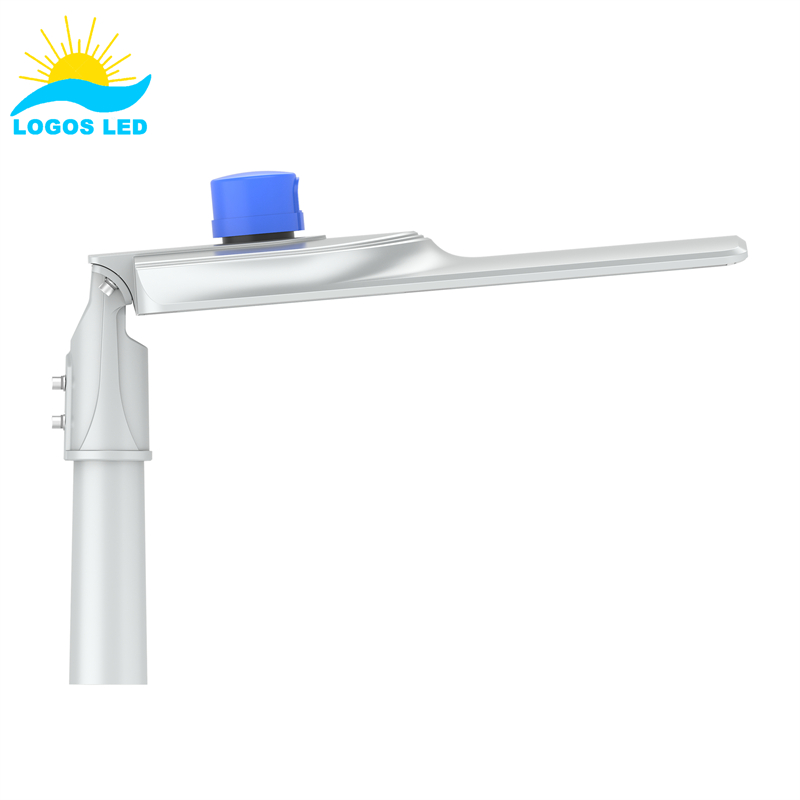
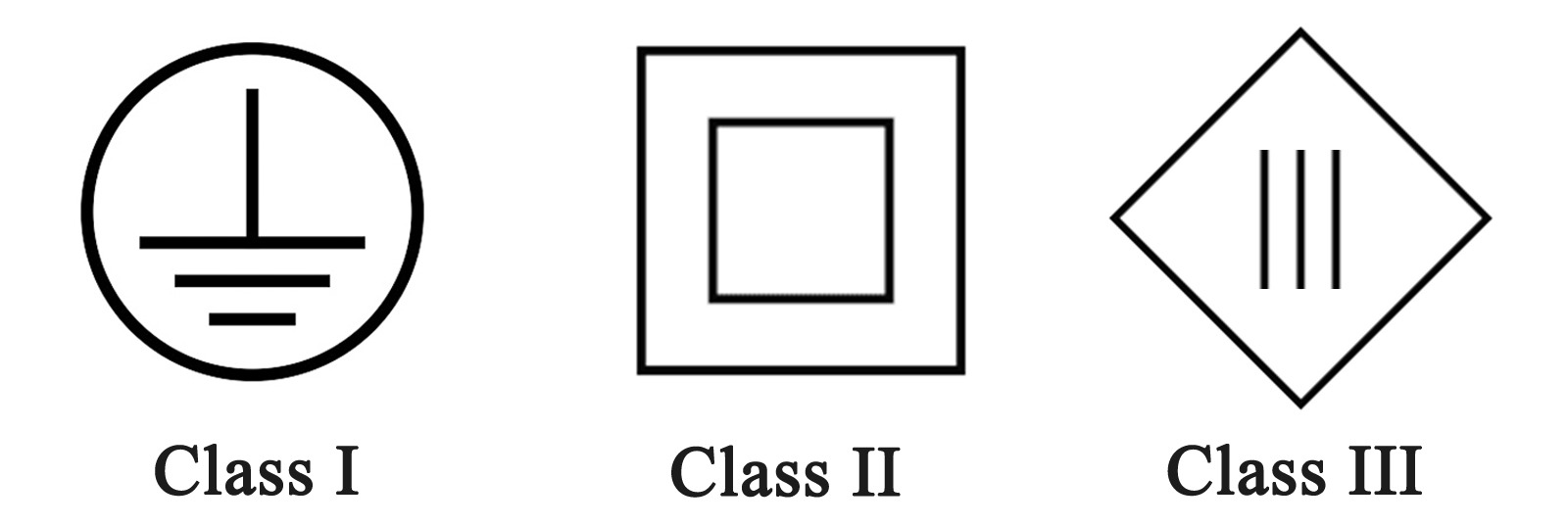
Luminaires are classified as Class I, II, or III based on their electrical safety. Class I luminaires have basic insulation with an earth connection. Think of street lamps. Class II luminaires have double or reinforced insulation without an earth connection. Think of portable fixtures. Class III luminaires operate on Safety Extra-Low Voltage, the safest option for sensitive environments like medical settings.
Let’s dive a little deeper into each class and see how they can impact your business operations.
Table of Contents
What are Class I, Class II and Class III Luminaires?
Luminaires are classified into three main categories based on how well they protect you from getting shocked.
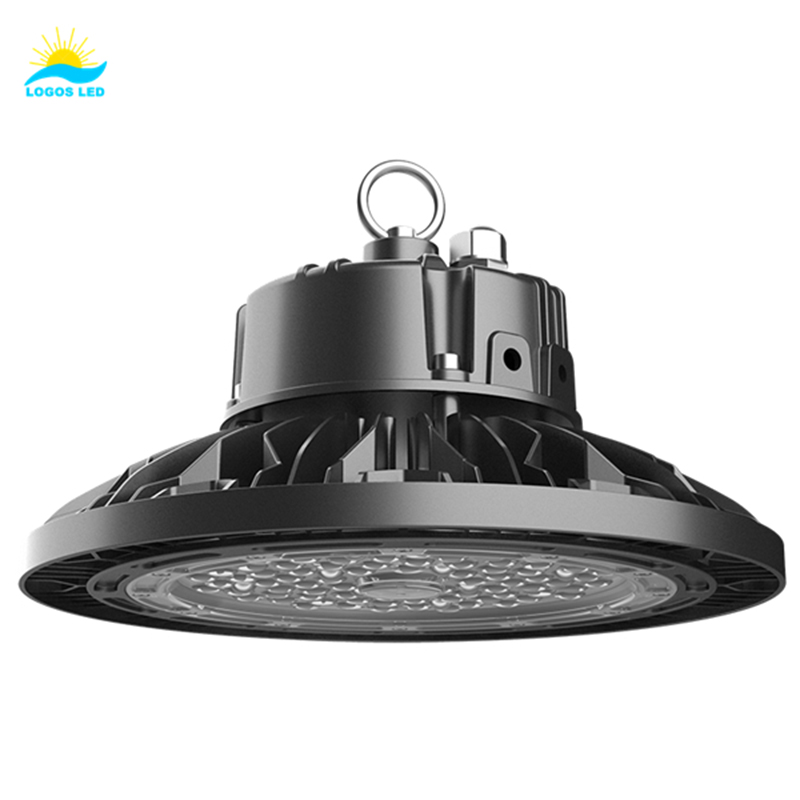
Class I Luminaires
Class I luminaires have basic insulation and a protective earth connection. Key features include:
Three-pin plug or three-wire power cord with an earth wire connection
All metal components are ‘earthed’
Basic insulation (e.g. plastic insulation of wires) plus earth wire protection
Typically used in sturdy plastic cases like street lamps, LED flood lights, LED high bay lights, LED sports lights, etc
Class II Luminaires
Class II luminaires offer protection based on double insulation or reinforced insulation, without relying on an earth connection. Characteristics include:
Two-wire power cord (no earth connection)
Supplementary insulation in addition to basic insulation
Designed to prevent direct contact with electric parts
Often used in LED panel lights, LED down lights and portable LED fixtures
Class III Luminaires
Class III luminaires operate on Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) supplied by an external transformer. Key aspects include:
Powered by SELV(Safety Extra-Low Voltage), typically below 60V, commonly used is 24V or 12V
Highest level of protection due to low voltage
Commonly used in indoor or outdoor applications and extreme weather conditions
Examples include LED strip lights and some medical devices
Class III luminaires offer the highest level of protection among the three classes, making them suitable for applications involving children or in medical environments.
What are Class 1, Class 2 Luminaires?
Class 1 and Class 2 luminaires are categorized based on their electrical output characteristics and safety features according to UL (Underwriters Laboratories) standards:
Class 1 Luminaires
Class 1 luminaires have output ranges that exceed the limitations set for Class 2 devices. Key features include:
High-voltage output
Require safety protection within the fixture
Can accommodate more LEDs, making them potentially more efficient
Pose a higher risk of fire or electric shock if not properly installed
Wiring methods must comply with NEC(National Electric Code) requirements for power circuits
Typically used for high power or long runs of LED lights
Class 2 Luminaires
Class 2 luminaires comply with UL1310 standard and are considered safer due to their limited output. Characteristics include:
Output is considered safe to contact
No major safety protection required at the LED/luminaire level
Operate using less than 60 volts in dry applications, 30 volts in wet applications
Current limited to less than 5 amps
Power limited to less than 100 watts
Lower risk of fire or electric shock
Can use smaller gauge wires and connectors
Typically used for low power or short runs of LED lights
It’s important to note that Class 1 and Class 2 designations are based on the National Electric Code (NEC) and are distinct from the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) classifications of Class I, II, and III, which refer to a power supply’s internal construction and electrical insulation.
Differences between Class I, II, III and Class 1, 2 Luminaires
The primary differences between IEC and UL classifications for luminaires are due to their focus and regulatory background. IEC classifications (Class I, II, III) are based on the internal construction and electrical insulation of the luminaires to protect people from getting shocked. They ensure different levels of safety for the user through different types of insulation and protection:
- Class I offers protection through earth connections and basic insulation.
- Class II increases safety by using double or reinforced insulation, eliminating the need for earth connections.
- Class III provides the highest safety through the use of Safety Extra-Low Voltage systems, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock.
On the other hand, UL classifications (Class 1, 2) are based on the output characteristics and the electrical safety requirements based on the power output of the luminaires. They look at the risk based on the electrical output. They tell you what you need to have in place to deal with the danger:
- Class 1 devices handle higher voltages and require robust safety measures within the fixture to prevent fire and shock hazards.
- Class 2 devices are deemed safe to contact and operate with limited power output, thereby reducing the need for stringent safety protections within the fixture.
In other words, IEC protects you from the inside of the box. UL protects you from the outside of the box.
| Feature | Class I (IEC) | Class II (IEC) | Class III (IEC) | Class 1 (UL) | Class 2 (UL) |
| Electrical Connection | Three-pin plug or three-wire power cord with earth wire | Two-wire power cord (no earth connection) | Powered by SELV | High-voltage output | Limited output, safe to contact |
| Insulation | Basic insulation with earth wire protection | Double or reinforced insulation | Operates on low voltage for maximum safety | Requires safety protection within the fixture | No major safety protection required at luminaire level |
| Safety Features | Metal components are earthed | Prevents direct contact with electrical parts | Highest level of protection | High risk of fire or electric shock if not properly installed | Lower risk of fire or electric shock |
| Voltage Levels | Standard voltage | Standard voltage | typically below 60V, commonly used is 24V or 12V | Exceeds Class 2 limitations | Operates under 60 volts (dry), 30 volts (wet) |
| Current and Power | Standard | Standard | Depends on the external transformer | Can accommodate more LEDs | Current <5 amps, Power <100 watts |
| Typical Applications | LED street lamps, LED flood lights, LED high bay lights, LED sports lights, etc | LED panel lights, LED down lights and portable LED fixtures | LED strip lights, some medical devices | High power or long LED light runs | Low power or short LED light runs |
FAQs About Classes of Luminaires
What are the Three Classifications of Light?
In the electrical equipment world, especially with luminaires, there are three main classifications that tell you how well a fixture protects you from getting shocked, dust, water, and mechanical impact. Those are Class I, Class II, and Class III. Each class is designed for different environments and safety requirements. Class I needs an earth connection to protect you. Class II is double insulated. Class III operates on low voltage, so it’s safer in environments where you’re more likely to get shocked.
What is the Definition of Light Class 3?
Class III luminaires use safety extra-low voltage (SELV) not exceeding 60 volts. They’re considered safe from electric shocks. This makes them perfect for high-risk areas like schools, hospitals, and outdoor areas where higher voltages could be dangerous. These fixtures are especially important in places where the electrical insulation might not be perfect.
What is Class I and Class II?
Class I luminaires are designed to be protected by a connection to electrical earth. This is the connection that safely channels any fault current away. They’re used where there’s a higher chance of your body becoming the path for fault currents. Class II luminaires, also known as double-insulated luminaires, don’t rely on an earth connection to protect you. Instead, they have two layers of insulation to keep you from touching any live parts. These are the ones you use in your house.

What is a Class 1 and 2 Driver?
In the LED world, a Class 1 driver requires a ground connection as part of its safety. Class 2 drivers, which are used with Class II luminaires, are limited to 100 watts at 30 volts AC or 60 volts DC. This limits the risk of fire and electric shock, so they don’t need a ground. These drivers meet specific safety standards that limit the output voltage or current to safe levels.
What Does Class II Mean?
Class II equipment is also known as double-insulated equipment. This means it has two layers of insulation between the live parts and you. This is a critical classification for designing safer electrical devices, especially in non-industrial settings where it’s not practical to have grounded equipment.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Class I, Class II, and Class III luminaires is essential to your electrical safety, efficiency, and effectiveness. Each class has different safety standards and use cases, so you can make the best choice for your business. You want to buy lights that give you enough light, but you also want to make sure they meet the electrical safety standards.
If you need help with lighting or have any questions, please feel free to reach out to us directly. Our team of lighting experts is here to help.
Request A Free Quote Now!
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!