Poorly planned street lighting creates dark spots, reducing visibility and making roads unsafe. This can lead to accidents, discomfort, and wasted energy. But with the right mounting arrangements, street lights can provide even illumination, improve safety, and reduce energy costs. Let’s explore the best way to set up street lighting for your project.
Street light mounting arrangements play a major role in lighting uniformity, efficiency, and effectiveness. The most common setups include single-sided, staggered, opposite, and central mounting. Each one is chosen based on road width, traffic flow, and surrounding conditions. Picking the right arrangement improves safety, cuts energy costs, and ensures compliance with lighting standards.
Not sure which setup works best for your project? Keep reading to find out.
Table of Contents
What Are the Key Specifications for LED Street Lights?
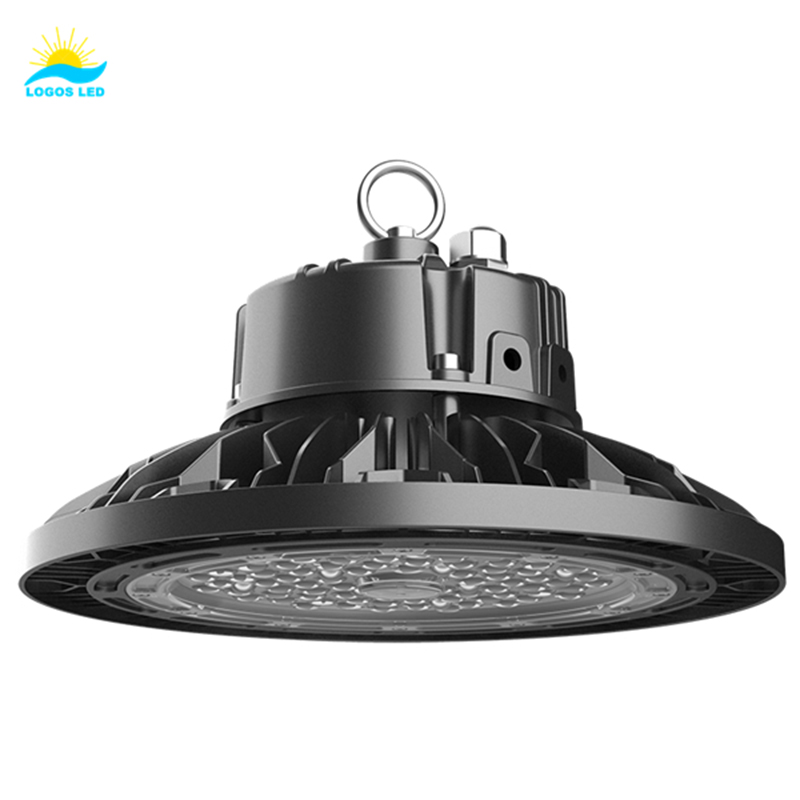
LED street lights are designed for maximum illumination, energy efficiency, and long-lasting performance. They’re widely used in urban streets, highways, and residential areas. Below, we break down their key specifications.
1. Wattage and Lumen Output
Wattage Range: LED street lights typically range from 30W to 300W. Lower wattages suit residential streets, while higher wattages light up highways and industrial zones.
Lumen Output: These lights provide 3,000 to 50,000 lumens, ensuring proper brightness for various applications.
Efficiency: With a high lumen-per-watt ratio, LEDs use less power than traditional lights like HID lamps, significantly lowering energy costs.
2. Color Temperature
3000K (Warm White): Produces a soft, yellowish light ideal for residential streets and parks.
4000K (Neutral White): Offers balanced lighting, perfect for city streets and pedestrian zones.
5000K-6500K (Cool White/Daylight): Delivers bright, clear illumination for highways and busy roads.
Choosing the Right Color Temperature: Cooler tones enhance visibility in high-traffic areas, while warmer tones reduce glare in quiet zones.
3. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
IP65 and Above: Most LED street lights have an IP65 rating, protecting against dust and water jets.
Higher Protection: IP66 and IP67 models offer extra durability for extreme weather conditions.
4. Color Rendering Index (CRI)
CRI 70+: Ensures accurate color visibility, making roads safer for drivers and pedestrians.
Higher CRI (80+): Used in urban areas and pedestrian crossings for improved clarity.
5. Lifespan and Maintenance
50,000+ Hours: These lights last over 11 years with daily 12-hour use.
Low Maintenance: Fewer replacements mean lower costs and less downtime.
Built for Durability: Advanced heat dissipation ensures stable performance in all weather conditions.
6. LED Driver Quality
Reliable Drivers: High-quality drivers, like those from Meanwell, ensure steady power supply and protection from voltage fluctuations.
Dimmable Options: Many drivers allow brightness adjustments, boosting energy savings and extending LED lifespan.
Additional Features to Consider
Smart Controls: IoT-enabled lights allow remote monitoring, scheduling, and fault detection.
Motion Sensors & Photocells: Automatically adjust brightness based on movement and ambient light.
Advanced Heat Dissipation: Keeps LEDs cool, preventing performance issues.
With these features, LED street lights provide long-term efficiency, durability, and cost savings for outdoor lighting projects.
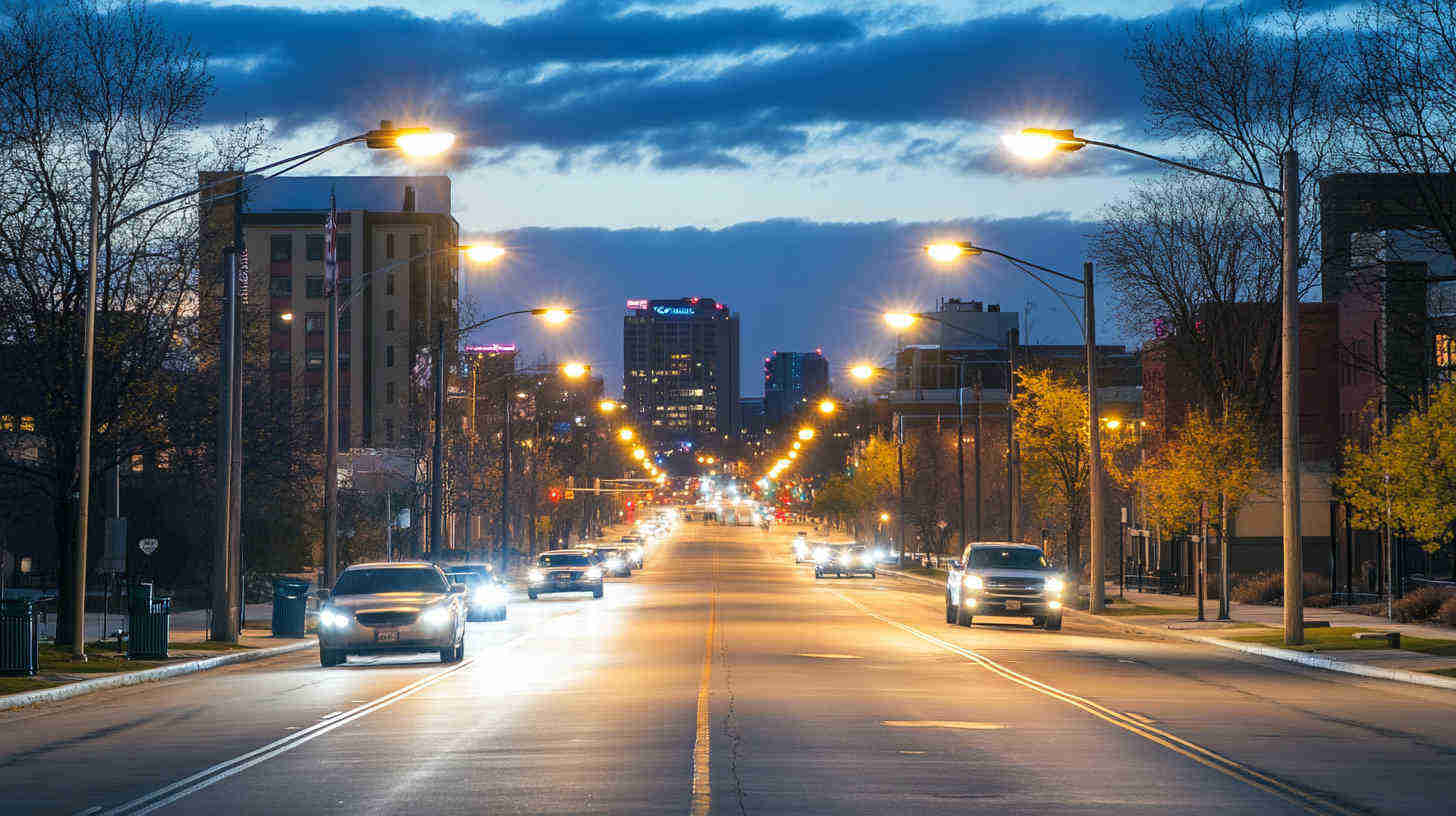

What Are the Different Street Light Mounting Arrangements?
How street lights are mounted determines their effectiveness. Here are the most common setups:
1. Single-Sided Mounting
Setup: Lights are placed on one side of the road.
Best For: Narrow streets, sidewalks, and residential areas.
Pros: Simple and cost-effective.
Cons: Can cause uneven lighting on wider roads.
2. Staggered Mounting
Setup: Lights are installed alternately on both sides of the road in a zig-zag pattern.
Best For: Medium-width roads and moderate traffic zones.
Pros: Ensures balanced lighting.
Cons: Requires more poles than single-sided mounting.
3. Opposite Mounting
Setup: Lights are placed directly opposite each other on both sides of the road.
Best For: Wide roads and highways.
Pros: Provides uniform, symmetrical lighting.
Cons: Higher installation costs due to extra poles and fixtures.
4. Central Mounting
Setup: Lights are installed along the median of the road.
Best For: Roads with central dividers or dual carriageways.
Pros: Reduces pole clutter on sidewalks.
Cons: Not suitable for roads without a median.
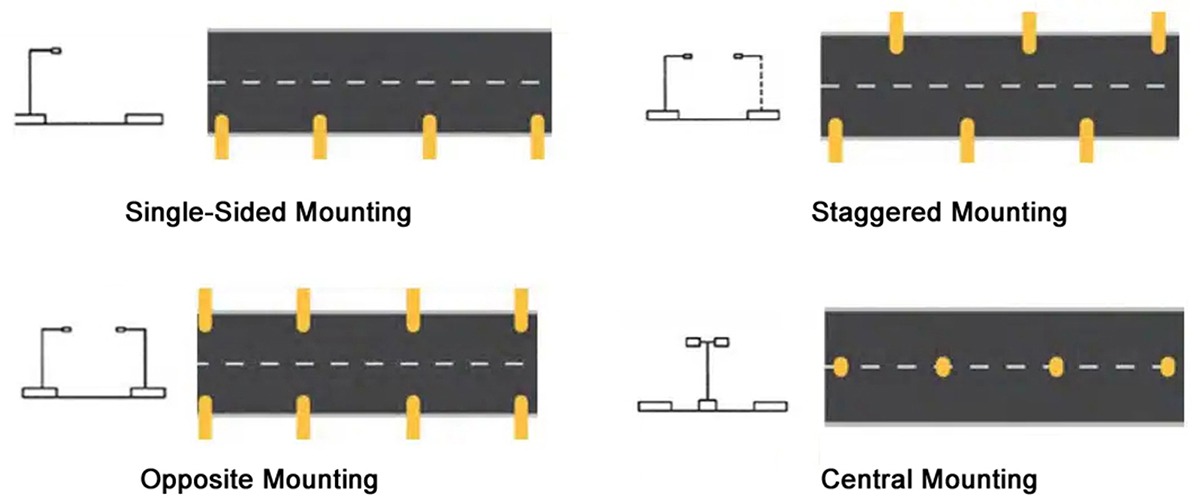
Different Street Light Mounting ArrangementsChoosing the right street light mounting arrangement ensures better illumination, enhances safety, and optimizes energy use.
Things to Consider for Proper Placement of Light Poles
Proper placement of light poles is key to achieving uniform illumination, safety, and a visually appealing streetscape. Here are the most important factors to keep in mind when positioning poles for street lighting.
Pole Distance from the Roadway
Description: The distance between the pole base and the road edge affects safety and visibility.
Recommendation: Poles should typically be placed 1.5 to 3 meters away from the road to prevent collisions while ensuring proper illumination.
Factors: Sidewalk presence, road type (urban or highway), and local regulations should be considered when determining placement.
Arm Length
Description: The length of the arm holding the luminaire determines how far the light extends over the roadway.
Recommendation: Standard arm lengths range from 1 to 3 meters, depending on the road width.
Impact: Longer arms help illuminate wider roads, ensuring even light distribution, while shorter arms work well for narrow streets.
Overhang
Description: Overhang refers to how far the luminaire extends beyond the arm, positioning the light directly over the road.
Recommendation: Ideally, the overhang should align with the road’s centerline for maximum coverage.
Importance: Proper overhang placement minimizes dark spots and ensures even lighting across the roadway.
Arm Tilt Angle
Description: The tilt angle affects how the light spreads and where it is directed.
Recommendation: A tilt angle of 0° to 15° is commonly used, depending on road conditions and luminaire type.
Effect: Adjusting the angle can reduce glare and ensure the light is distributed efficiently without unnecessary spill.
Pole-to-Pole Distance (Spacing)
Description: The spacing between poles influences illumination uniformity and intensity.
Recommendation:
- Urban streets: 30 to 50 meters
- Highways: 50 to 100 meters
- Pedestrian paths: 15 to 20 meters
Factors: Spacing should be calculated based on road width, luminaire wattage, mounting height, and required light levels.
Considering these factors ensures efficient energy use, improved safety, and optimal street lighting performance. Need expert advice? Contact us for professional street lighting solutions!

How Are Street Lights Placed?
Street lights are positioned with precision to maximize visibility, enhance safety, and minimize energy consumption. Several critical factors influence their placement:
1. Road Type and Function
Street lighting placement varies depending on the type of road:
- Highways & Expressways: Lights are spaced farther apart, typically on one or both sides, ensuring broad and uniform coverage.
- Urban Streets: More frequent placement is required to maintain consistent illumination for vehicles and pedestrians.
- Pedestrian Walkways & Residential Areas: Lower mounting heights and closer spacing provide better visibility for pedestrians while reducing glare.
2. Pole Spacing and Mounting Height
The distance between poles depends on several factors:
- Road Width: Wider roads require taller poles and increased spacing.
- Luminaire Output: Brighter lights can be spaced further apart while maintaining illumination levels.
- Mounting Height: Higher poles reduce the number of fixtures needed but require precise angling to avoid dark spots.
3. Light Distribution Patterns
Street lights are arranged to minimize overlap while eliminating dark spots. Different beam angles and optical distributions are used based on road layout:
- Symmetrical Distribution: Best for open spaces, parking lots, and wide roads.
- Asymmetrical Distribution: Ideal for roadways where focused lighting is required on lanes and sidewalks.
- Cutoff Lighting: Used to prevent light pollution by directing illumination downward.
4. Avoiding Obstructions
Proper positioning ensures that lights are free from obstructions such as:
- Trees and Foliage: Overgrown trees can block illumination and create shadows.
- Buildings and Signage: Street lights should not create glare or reflection issues for drivers and pedestrians.
- Utility Lines and Poles: Placement must comply with safety regulations to avoid electrical hazards.
5. Energy Efficiency and Smart Controls
Modern street lights incorporate:
- LED Technology: Reduces energy consumption while providing high-lumen output.
- Smart Lighting Systems: Adaptive brightness and motion sensors adjust illumination based on traffic density and environmental conditions.
- Solar Integration: In remote or off-grid areas, solar-powered street lights provide a sustainable lighting solution.
Strategically placed street lighting ensures road safety, enhances urban aesthetics, and supports energy conservation. To explore advanced LED street lighting solutions, check out our LED Street Lights Collection.

What Is the Spacing for Street Lights?
Spacing is crucial for maintaining uniform brightness across different road types:
- Standard Roads: Typically 30-50 meters, based on luminaire wattage and mounting height.
- Highways: Wider spacing of 50-100 meters is used for high-output fixtures.
- Pedestrian Areas: Closer spacing of 15-20 meters ensures better visibility.
Factors like road width, beam angle, and required lux levels determine precise spacing.
What Is the Best Angle for Street Lights?
The angle of street lights affects both distribution and glare control:
- Recommended Angle: Between 0° and 15°, ensuring light reaches the road without causing glare.
- Adjustable Fixtures: Many modern LED lights allow for tilt adjustments to optimize targeting.
- Application-Specific: Wider angles are used in pedestrian areas, while narrower angles suit highways for precise illumination.
Setting the correct angle improves visibility and energy efficiency.
How High Should LED Street Light Poles Be?
Pole height depends on road conditions and lighting needs:
- Residential Streets: 6-9 meters
- Urban Roads: 9-12 meters
- Highways: 12-15 meters
- Sports Fields & Large Areas: 20-30 meters, using high-output luminaires
The right pole height ensures even light distribution and reduces unwanted shadows.

Conclusion
Choosing the right street light mounting arrangement and following proper placement guidelines ensure optimal lighting performance, safety, and efficiency. Whether it’s single-sided mounting for narrow roads or central placement for highways, each setup serves a specific purpose. Need help designing your street lighting system? Contact us today—our experts are ready to guide you to the best solution for your project!
Request A Free Quote Now!
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!