Table of Contents
The Importance of EMC
As early as the early 1980s, infant mortality was quite high in the maternity ward area of a hospital in New Jersey. Late at night, the warning light on the baby’s monitor always goes out for no reason. The nurses were so annoyed that they turned off the monitors and went back and forth one by one.
After a preliminary investigation, the professor ascertained the truth of the matter. It turned out that the transmitter of a nearby television station was approved by the American Communications Commission and its output power can be increased quite high after about midnight, but it must be before the morning. And during other specified time, returns to the original level. The connection cable between the nurse’s station and each baby’s monitor resonates at these interference frequencies, and the induced voltage causes the monitor’s warning light to go out. Before the hospital found the problem, almost six children had died.
There is another example: there was such a customer complaint response when a switching power supply was turned on in the computer room, the company’s 100M-speed LAN fell and stopped, but the 10M-speed network was not affected. Turning off the power and the network returns to normal.
Later experiments found that the high-frequency interference signal of the switching power supply was coupled to the network line, causing the network to fail.
What is EMC
EMC was born with the rapid development of the modern electronics industry. By the end of the last century, with the rapid increase in electronic and electrical equipment. EMC has expanded into many fields, and it is no exaggeration to say that where there are electronic products, there are EMC problems.
Basic Knowledge:
EMC: Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMI: Electromagnetic Interference
EMS: Electromagnetic Susceptibility
ESD: Electrostatic Discharges
RS: Radiated Susceptibility
EFT: Electronic fast transients
SURGE
CS: Conducted Susceptibility
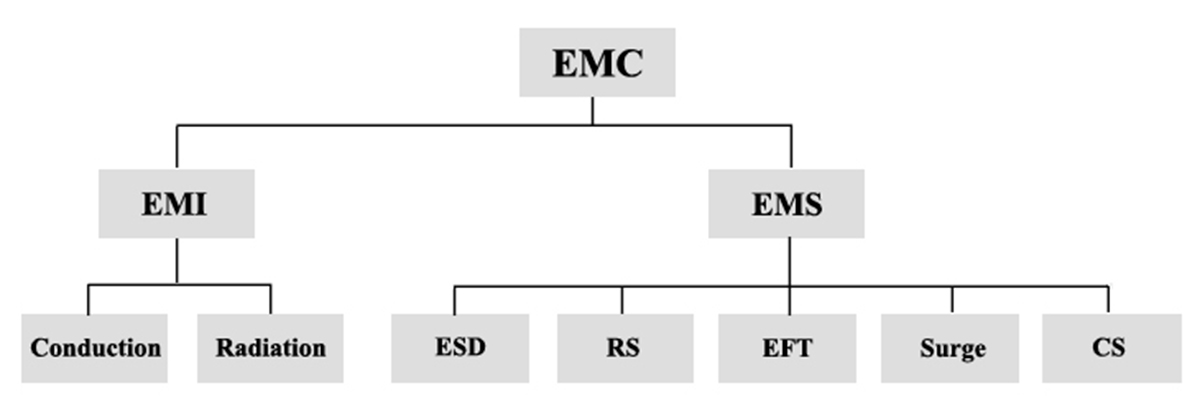
EMC
That’s to say, EMC =EMI +EMS
Here is a brief introduction of EMC standards in different markets
1. EU
Certificate: EMC
The test standards are divided into two parts: EMI and EMS:
1. EMI standards are EN55022, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3; EN55022 is Radiation Test and Conduction Test;
2. EMS standards are EN55024, which contains total 7 parts of testing:
EN61000-3-2 is Harmonic Test
EN61000-3-3 is Flicker Test
EN61000-4-2 is ESD Test
EN61000-4-3 is RS Test EN61000-4-4 is EFT Test
EN61000-4-5 is Surge Test
EN61000-4-6 is CS Test
EN61000-4-8 is PFMF Test EN61000-4-11 is DIP Test
2. US
Certificate: FCC
Test standard: FCC Part 15
3. Oceanian
Certificate: C-tick
Test standard: AS/NZS CISPR 22:2006
If you have any questions about EMC or your LED lighting fixtures, welcome to contact us directly.
Request A Free Quote Now!
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!