In hazardous environments, regular lights can blow things up. Explosions caused by unsafe lights will ruin your whole day. The solution? Explosion-proof lights are safe and reliable.
Explosion-proof lighting refers to specialized lighting fixtures designed to prevent the ignition of flammable substances in hazardous environments. These lights are engineered to isolate potential ignition sources within the fixture, preventing sparks or flames from interacting with explosive gases, vapors, or dust in the surrounding atmosphere
Understanding the ins and outs of explosion-proof lighting will help you choose the right explosion-proof light for you. Let’s get into the details.
Table of Contents
What are the different types of Hazardous Area/Explosion Proof Lights?
Hazardous area lighting, also known as explosion-proof lighting, is special lighting fixtures that are made to work in places where there are flammable gases, vapors, or dust. These are found in industries like oil and gas, mining, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals. Hazardous area lighting is divided up into different classes, divisions, and groups to ensure safety. Below are the key categories:
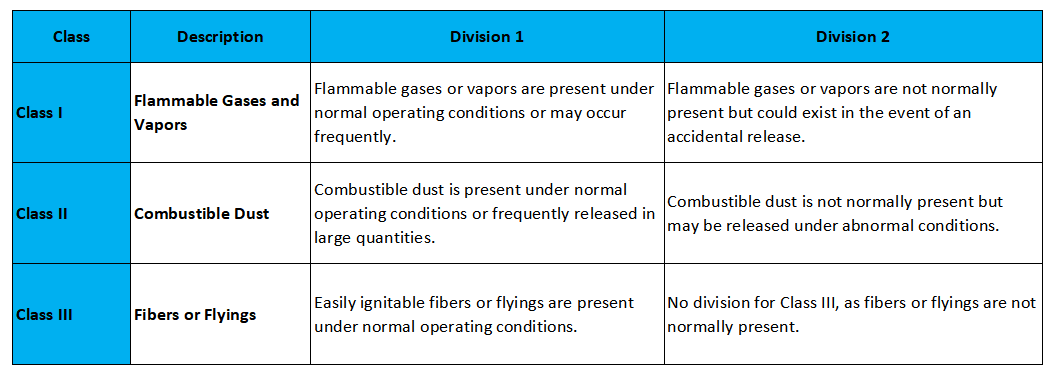
Classes and Divisions for Hazardous Area Lighting
Class I (Flammable Gases and Vapors)
This class covers areas where flammable gases or vapors may be present in the air. It is divided into two divisions:
- Division 1: Flammable gases or vapors are present under normal operating conditions, or they may occur frequently.
- Division 2: Flammable gases or vapors are not normally present but could exist in the event of an accidental release.
Class II (Combustible Dust)
This class pertains to environments where combustible dust is present. It is divided into two divisions:
- Division 1: Dust is present during normal operations or occasionally released in large quantities.
- Division 2: Dust is not normally present but may be released under abnormal conditions.
Class III (Fibers or Flyings)
This class covers areas where easily ignitable fibers or flyings are present, such as textile manufacturing or woodworking plants. It does not have further division into subcategories.
Classes and Divisions for Hazardous Area Lighting
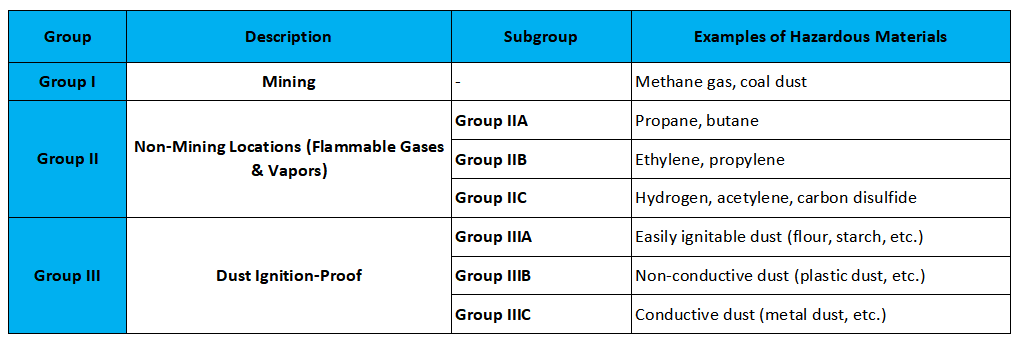
Explosion Proof Lighting Groups
Explosion-proof lighting is broken down into different groups based on the type of hazardous material. These groups determine how much protection the lighting equipment needs:
Group I (Mining)
This group is for areas where the risk of ignition arises from methane gas and coal dust. It is mainly applicable to underground mining environments.
Group II (Non-Mining Locations)
This group applies to areas with the potential presence of flammable gases or vapors. It is subdivided into:
- Group IIA: For areas with gases like propane and butane.
- Group IIB: For areas with gases such as ethylene.
- Group IIC: For the most hazardous areas, including locations with hydrogen or acetylene.
Group III (Dust Ignition-Proof)
This group includes environments where combustible dust is present, such as food processing or metalworking. It is subdivided into:
- Group IIIA: For environments with easily ignitable dust like flour.
- Group IIIB: For areas with non-conductive dust, such as plastic dust.
- Group IIIC: For areas with conductive dust, such as metal dust.
Explosion Proof Lighting Groups
Each class, division, and group specification is a way to say, “This lighting system will not cause a fire or explosion in a hazardous environment.” This is important if you don’t want your workers to die and your factory to blow up. When selecting hazardous area lighting, you need to make sure the lighting equipment you buy is compliant with the specific environmental conditions of the area.
Key Features of Explosion-Proof Lighting
Construction
These lights are made of tough, non-sparking materials, have thick glass globes around the light bulb, have strong housings, and have a lot of stuff inside to keep sparks or explosions from getting out.
Safety Mechanism
Their main job is to keep the fixture itself from blowing up, not to survive an explosion. They work by keeping the sparky stuff inside the lamp away from the things that will blow up.
Applications
Explosion-proof lighting is commonly used in:
– Oil and gas industry
– Chemical processing plants
– Paint booths
– Food processing facilities
– Mining operations
– Other hazardous locations with flammable gases, vapors, or dust.
Benefits and Importance
Safety
These lights significantly reduce the risk of explosions and protect workers from potential injuries in hazardous workplaces.
Regulatory Compliance
Explosion-proof lighting must adhere to specific standards such as ATEX (Europe), IECEx (Global), and NEC (United States).
Energy Efficiency
LED explosion-proof lights can consume up to 90% less energy than standard fixtures, leading to reduced operational costs.
Durability
These lights are designed to withstand harsh conditions and typically have a long lifespan, often lasting 50,000 to 100,000 hours of continuous use.
By providing safe and sufficient lighting in hazardous environments, explosion-proof lighting plays a crucial role in maintaining workplace safety and operational efficiency in industries dealing with potentially explosive materials.
What Makes a Light Explosion-Proof?
Explosion-proof lighting fixtures are designed to prevent internal explosions from igniting the hazardous environment. They have tough housings that contain any sparks, heat, or flames generated inside the fixture. By isolating the electrical components and sealing the housing, these lights ensure that even if something goes wrong inside the fixture, the environment outside the light is safe. This is why explosion-proof lighting is so critical in dangerous industrial locations.

What Are the Requirements for Explosion-Proof?
For a light to qualify as explosion-proof, it must meet specific safety criteria. These include:
- Durable Enclosures: The housing must withstand extreme pressures without cracking or rupturing.
- Certified Seals: Proper seals prevent the escape of flames or sparks from the fixture.
- Thermal Management: Effective heat dissipation ensures safe operation in high-temperature environments.
- Compliance with Standards: Manufacturers must meet explosion-proof lighting standards like Class 1 Division 1 and IECEx certification.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the lighting fixture operates reliably in hazardous areas without posing safety risks.
What Is the Standard for Explosion-Proof?
Explosion-proof lighting standards vary by region and industry, but the most common certifications include:
- Class 1 Division 1: Used in environments with flammable gases or vapors present during normal operations.
- ATEX Certification: Common in Europe, ensuring safety in explosive atmospheres.
- IECEx Certification: An international standard that validates explosion-proof capabilities.
- UL Certification: Recognized in North America, covering rigorous testing for safety compliance.
These standards guarantee that explosion-proof lighting is suitable for specific hazardous conditions.
What Materials Are Explosion-Proof Lighting?
Explosion-proof lighting fixtures are crafted from materials that provide strength, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. Common materials include:
- Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for harsh environments.
- Stainless Steel: Robust and durable, suitable for chemical plants and offshore installations.
- Tempered Glass: Used for lenses, ensuring clarity and resistance to high impacts.
- Polycarbonate: A durable and lightweight option for certain parts of the fixture.
These materials ensure the fixture’s longevity and performance in challenging industrial settings.
What Is the Difference Between Explosion-Proof and Explosion Resistant?
While both terms address safety in hazardous environments, there are key differences:
- Explosion-Proof: Prevents internal explosions from igniting external environments. Designed for highly volatile zones.
- Explosion-Resistant: Withstands external explosions without damage, focusing on structural integrity rather than containment.
Explosion-proof fixtures are essential in environments where flammable substances are constantly present, while explosion-resistant equipment is used in areas with occasional risks.
Where Are Explosion-Proof Lights Required?
Explosion-proof lights are vital in industries and environments prone to explosive hazards, such as:
- Oil and Gas Rigs: High concentrations of flammable gases require reliable lighting solutions.
- Chemical Plants: Hazardous chemicals and vapors demand safe lighting.
- Mining Operations: Dust and combustible particles necessitate explosion-proof fixtures.
- Manufacturing Facilities: Areas with high temperatures or volatile substances benefit from these lights.
By using explosion-proof lighting in these settings, businesses can ensure compliance with safety regulations and protect workers.
Is Explosion-Proof the Same as Fire-Rated?
No, explosion-proof and fire-rated lighting serve different purposes:
- Explosion-Proof Lighting: Contains internal sparks and prevents external ignition, suitable for hazardous zones.
- Fire-Rated Lighting: Designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, ideal for buildings with strict fire safety codes.
While explosion-proof fixtures focus on preventing explosions, fire-rated fixtures emphasize fire containment, making them distinct yet complementary safety solutions.
Conclusion
Explosion-proof lighting is a critical safety feature in industries dealing with hazardous materials. By understanding its requirements, standards, and applications, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance workplace safety. Logos Lighting provides top-quality Explosion Proof LED lighting Class 1 Division 1 fixtures, adhering to global explosion-proof lighting standards. Contact us today to explore reliable solutions at competitive prices.
Request A Free Quote Now!
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!